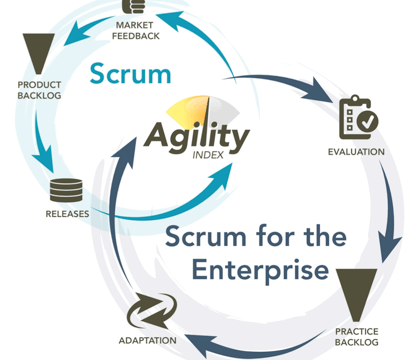
Scrum Theory – Scrum Framework
Scrum Theory is a part of Agile methodology. Agile is a time-boxed, iterative approach to software delivery that builds software incrementally from the start of the project, instead of trying to deliver it all at once near the end. It works by breaking projects down into little bits of user functionality called user stories, prioritizing […]